Understanding Fuse Cutouts: A Comprehensive Guide to Overcurrent Protection
Introduction:
Fuse cutouts are essential components in electrical distribution systems that provide overcurrent protection. They play a vital role in safeguarding electrical equipment and preventing damage caused by excessive currents. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of fuse cutouts, their working principles, types, installation, and maintenance practices, highlighting their significance in maintaining a reliable and safe electrical infrastructure.
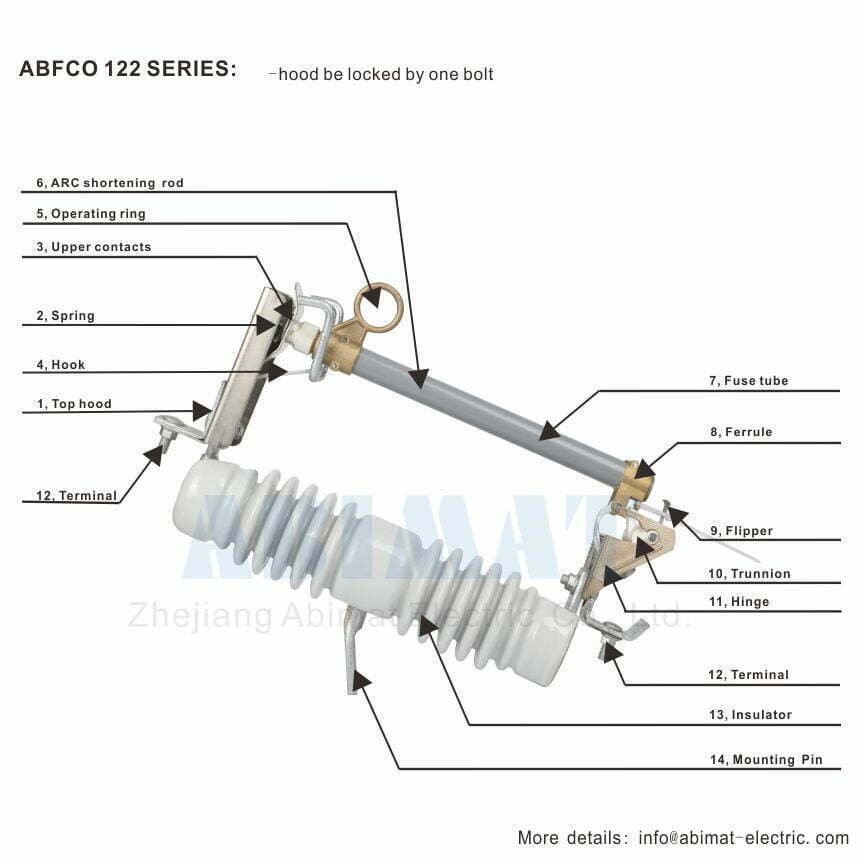
1. Overview of Fuse Cutouts:
ABIMAT Fuse cutouts, also known as fused disconnect switches or expulsion fuses, are protective devices designed to interrupt current flow in the event of overcurrent conditions. They consist of a fuse assembly and a disconnect switch, which are combined into a single unit. When an excessive current passes through the fuse cutout, the fuse element melts or “blows,” opening the circuit and disconnecting the faulty section from the power source.
2. Working Principles:
Fuse cutouts utilize the principle of thermal interruption to protect against overcurrents. The fuse element inside the cutout is made of a low-melting-point material, such as silver or copper. Under normal operating conditions, the current flows through the fuse element without any interruption. However, if the current exceeds a predetermined rating, the heat generated by the excessive current causes the fuse element to melt, creating an open circuit.
3. Types of Fuse Cutouts:
There are several types of ABIMAT fuse cutouts available, each designed for specific applications and voltage levels. Common types include:
- Expulsion Fuse Cutouts: These cutouts utilize the expulsion effect of gases to extinguish the arc and interrupt the current.
- Dropout Fuse Cutouts: Dropout cutouts are designed to provide a visible indication when the fuse element operates.
- Current-Limiting Fuse Cutouts: These cutouts are engineered to limit the amount of fault current that can flow through the system.
4. Installation and Maintenance:
Proper installation and regular maintenance of fuse cutouts are crucial for ensuring their reliable performance. Here are some key considerations:
- Correct selection of fuse cutout type based on the system requirements.
- Installation following manufacturer guidelines and adhering to safety regulations.
- Regular inspections to identify signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Prompt replacement of blown fuses to maintain effective overcurrent protection.
5. Benefits and Applications:
Fuse cutouts offer several advantages, making them widely used in electrical distribution systems. Some key benefits include:
- Reliable overcurrent protection for electrical equipment.
- Cost-effective solution compared to alternative protective devices.
- Quick and easy replacement of blown fuses, minimizing downtime.
- Suitable for a broad range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Conclusion:
Fuse cutouts are indispensable components in electrical systems, ensuring overcurrent protection and preventing damage to equipment. Understanding their working principles, types, and proper installation and maintenance practices is essential for maintaining a safe and reliable electrical infrastructure. By implementing fuse cutouts effectively, we can mitigate the risks associated with overcurrents and enhance the overall performance of electrical distribution systems.

